

A leaf is a part of a plant attached to a stem resembling a flat structure. Leaves help plants collect sunlight, which they can then turn into energy (food) through a process called photosynthesis. Their flatness helps them in this task and they are thin to allow the sunlight easy entry into their cells. Leaves come in many shapes, sizes and colours. Leaves also help the plant exchange gases in the atmosphere, breathing in carbon dioxide and breathing out oxygen. This helps clean the air and creates the oxygen we breathe.

Leaf arrangement refers to the way leaves are positioned on a stem. This information is important because it helps people identify and group different kinds of plants and shrubs. In botany, this is called phyllotaxy and there are three different types in leaves commonly spoken of when referring to trees and shrubs.
The different parts of a leaf each play an important role in nurturing and sustaining the plant so the leaf can work its magic. This diagram shows the three main parts of a leaf’s anatomy.
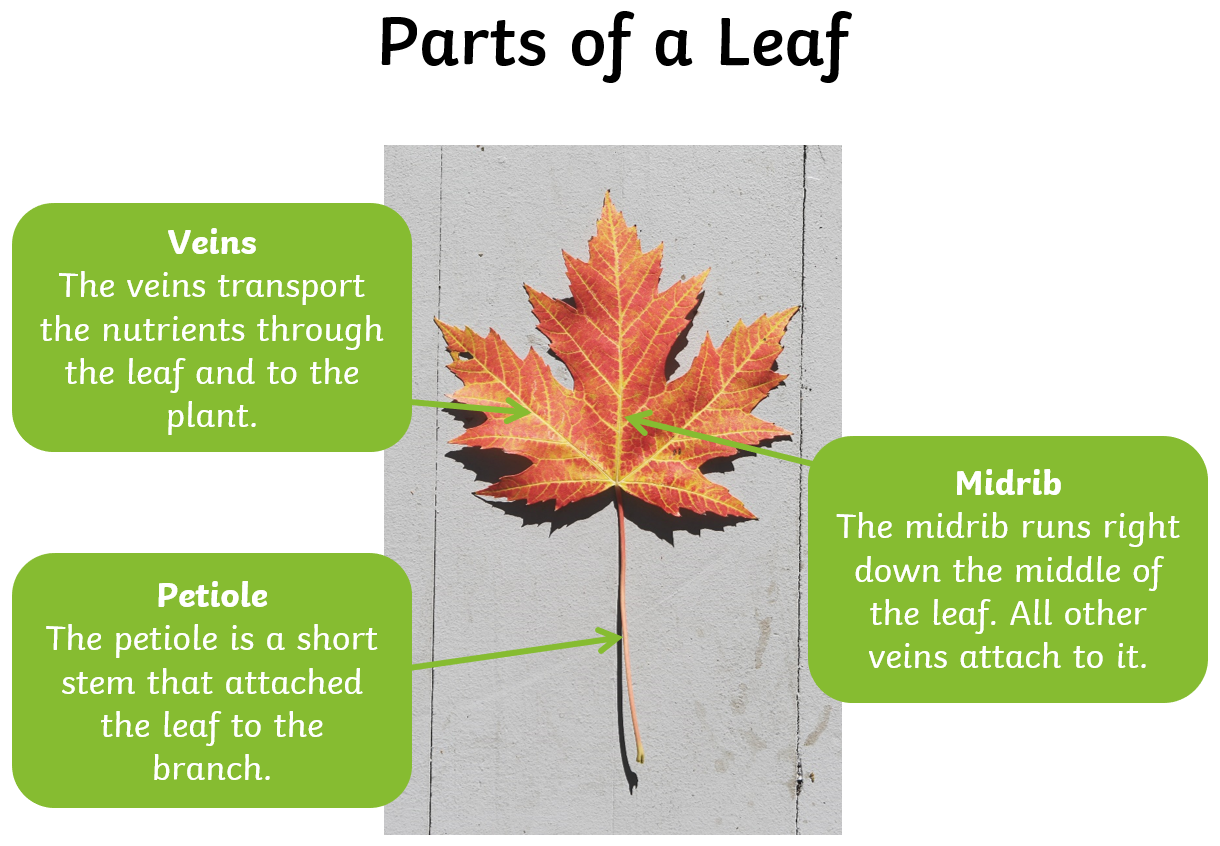
If you’d like to teach your students more about leaves and plant science, you’ve come to the right place. Our website is full of fun and interesting teaching materials you can use, from blank leaf templates to beautifully illustrated PowerPoints.
For example, this Leaf Life STEM PowerPoint is a great place to start when talking to your students about how leaves function and the role they play in sustaining plants.
We also have these lovely leaf templates for decorating your classroom. Create a beautiful display by adding a splash of green to your classroom walls or cork board.
Lastly, this Leaf Writing Template could also bring a great opportunity for students to create their own display. Simply ask them to write their name, or something relating to what they’re learning, on a leaf and stick it on this Large Tree template. It’s a great way to symbolise the important role that each individual plays in the class.
 Home
Home  Membership
Membership  Customer Support
Customer Support  Create
Create  Blog
Blog 























