Acorus calamus / Sweet flag /Bach / Vacha

General features: The botanical name of this flowering plant is Acorus calamus (AC), in English it is called Sweet flag whereas in Bengali, it is named as Bach and in Sanskrit it is termed as Vacha. From the early Vedic period, this herb is known to stimulate the intelligence in brain and subsequent behavior of self-expression. Besides the effect of rejuvenation of brain and nervous system, it also stimulates the appetite behavior. In India, the plant is considered as a valued drug since it acts as a rejuvenator. It can reduce the acidity of stomach also at small doses it cures anorexia but at large doses it may induce vomiting. Externally, it is often used to treat eruptions on the skin. Further, it is seen to be effective against dyspepsia and epilepsy. The herb belongs to Acoraceae family of Acorus genus. AC is an important and much appreciated medicinal herb due to its diverse health effects. The word ‘Acorus’ is evolved from Greek ‘Acoron’ introduced by the most celebrated ancient Greek physician, pharmacologist and scientist, Pedanius Dioscorides in his book “De Materia Medica”. That brought the word ‘Coreon’ meaning pupil since this herb was traditionally used to treat eye problems, particularly during inflammation. Afterward, it showed numerous medicinal actions like anti-spasmodic, carminative and anthelmintic effects. It has been in use to treat few neurological disorders like epilepsy and other chronic CNS disorders. It is commonly used for treating fevers, kidney stones, rheumatism, eczema and bronchial infections. The herb is a native of India, Central Asia, Europe and Southern Russia and Siberia. In India, AC grows in the North Eastern states like in Manipur, Nagaland, and Mizoram also on the north eastern Himalayan regions. Some varieties are also cultivated as a precious medicinal plant in the Sothern states of India like Tamilnadu, Andhra and Kerala. According to the ancient Indian Ayurveda, this medicinal herb helps enhance intelligence and improves the speech. The ancient text also claimed its ability to manage the epilepsy, schizophrenia and amnesia. Considering other traditional / folk medicinal uses over the centuries, AC is seen highly effective against digestive disorders and pain. As per its adversarial role, it is also considered to be slightly toxic although no exact clinical data are available. The major parts consumed for medicinal uses are rhizomes but in frequent occasions leaves are also expended. AC is herbaceous perennial plant that grows in the wetland or near any water front and normally reaches to a height of approximately 6 – 7 ft. It has the basal leaves rising from spreading rhizome. The leaves are yellowish-green with slight pink sheathing at the bases. They are sword shaped, narrow and flat, tapering to the long and acute point with parallel veins. AC can be distinguished from the others of similar kinds due to crimped edges of its leaves. Further, it spreads fragrances if crushed. Interestingly, those growing in wetland or near to water front only bears the flowers. The flower stems are solid and triangular that rise from the axils of outer leaves. The spadix arises from one side of the flower stem which is solid and cylindrical but tapers at the end, approximately 2 – 4 inches by length. The flowers have sweet fragrance. In Europe the flowering continues for about a month during late spring or at the beginning of summer. But it does not bear the fruit. The Asian variety occasionally grows fruits which are tiny berries filled with mucus. After ripening, it drops out and disperses in the water. The cylindrical rhizome is ½ inch diameter that bears numerous fibrous roots below. The color of rhizome exterior is brown but inside is pesky white.
Medicinal uses: The roots / rhizomes or leaves of Acorus calamus are used as a traditional medicine for curing or preventing numerous ailments. It is normally used, 1) to reduce fear and excitement and helping the schizophrenia sufferers, 2) in perfume industry owing to its sweet fragrance of essential oil, 3) to treat rheumatoid arthritis and body pain, 4) as a sedative, 5) for protecting cardiac system, 6) for skin infections like eczema or scabies, 7) to treat epilepsy, deafness and dizziness, 8) to treat constipation, 9) to cure fever, asthma, cold and bronchitis, 10) for its anti-neoplastic effect, 11) to relax muscle, 12) to enhance circulation in brain increasing awareness, 13) as anti-helminthic helping destroy the worms in intestine, 14) as antiviral, antifungal, to treat yeast infection and bacteria as well, 15) to cure colic pain, 16) as mouth freshener.
Adverse effect: The extract or essential oil exerts uterine contractions thus advisable not to use during pregnancy or lactation.
Chemical components and individual physiological role: Approximately 84 chemical constituents or more of different categories have been identified in AC rhizome and very similar in the leaf. There is a large reserve of essential oil having varieties of terpenes and phenolic derivatives eg, (Z) -Asarone (16 – 25 %) and (Z) – methyl-iso-eugenol (2 – 5 %), (E) – Caryophyllene, α – Humulene, Germacrene, Linalool, camphor and Iso-borneol and Cadinenes. In addition to those it has more like Acolamone, Acorenone, Acoragermacrone, Acoramone, Acorone, Calacone, Calcorene, Calamene, Calamenol, Calamone, Calamenone, Calarene and others. Below is the structure and brief description about their respective biological effects.
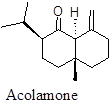
Salinen type sesquiterpene having sweet fragrance and anti-inflammatory action.
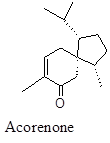
Sesquiterpene having inhibitory activity against Acetylcholinesterase and Butylcholinesterase that helps prevent Alzheimer’s and other cognitive dysfunction.
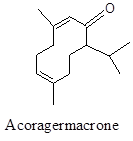
Powerful analgesic and anticonvulsant component.
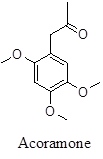
Phenyl propenoid component – suspected toxic, euphoric that may cause arousal.
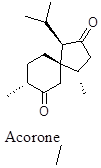
Bicyclic terpene having diuretic and antiurolithiatic effect and helps prevent kidney stone.
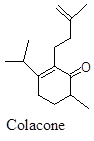
Monocyclic terpene showing antibacterial and antiinflammatory effect.
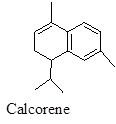
α- Isomer shows antimicrobial property including effects on gram (+) and gram (-) bacteria, Yeast (candida albicans).
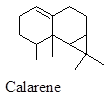
Tricyclic terpene having sedative and microbial effect.
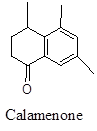
Psychoactive compound blocks CNS depression and anti-convulsing effect.
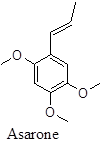
Phenyl propenoid. α- isomer is a hypocholestermic agent and binds to HMG-CoA. β- Isomer is a suspected carcinogen and toxic, providing bitter taste also displaying insecticidal antibacterial and neuroprotective properties.
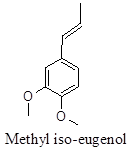
Phenyl propenoid, inhibitor of Acetyl-cholinesterase, α – glycosidase and α-amylase thus inhibits neurologic disorders like Alzheimer’s etc, acting as starch blockers having antidiabetic activity.
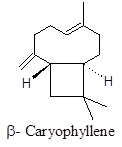
Bicyclic sesquiterpene provides aroma of black pepper binds and activates cannabinoid receptor (CB2) thus acting as potent analgesic, also a strong antiinflammatory agent particularly acting in brain and CNS tissues, considered to be anti-Alzheimer’s agent.
α-isomer of β-Caryophyllene acting as strong anti-inflammatory agent.
Exists in 4 isomeric form (A – E). A & D are the prominent ones. It is a sesquiterpene acting as pheromone also having strong insecticidal and antimicrobial properties.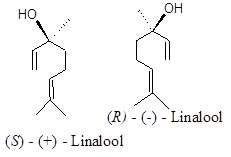
(S) – (+) isomer has coriander smell having mosquito repellent property. It also acts as insecticides for flea, fruit-fly, cockroaches and codling moth. (R) – (-) isomer has smell of Lavender and sweet basil.
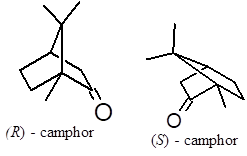
(R)- Isomer is more prominent than the (S)- analog. It acts as antimicrobial, pest-deterrent, local analgesic and used in making perfume. On the skin it causes heat sensation activating TRPV3 & TRPV1 receptors. Causing cool sensation in mouth by activating TRPM8 receptor also exerts tachy-cardia, vasodilation, perspiration and enhancing urination.
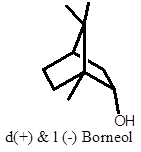
Exists in d (+) and l (-) isomers. It has potent insect repellent property.
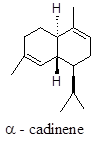
It exists in α to δ isomers. A bicyclic sesquiterpene. α-isomer has sweet smell also has antimicrobial and antiinflammatory effect.
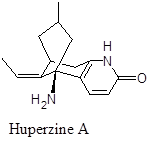
Naturally occurring sesquiterpene alkaloid that has neuroprotective property by inhibiting Acetylcholinesterase. It is a Pyridone and hetero-tricyclic compound. It is now under consideration for possible treatment of neuro-degenerative diseases especially Alzheimer’s.
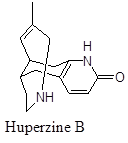
It is another isomer having identical biological action acting as Acetylcholinesterase inhibitor. It could be helpful also to treat various neurodegenerative diseases.
It is tropoloisoquinoline alkaloid isolated from the rhizome of Acorus calamus. It exhibits significantly inhibitory activity against Aβ25 – 35 induced neuronal (PC12) cell death.
It helps improve cholinergic function and lowers the generation of inflammatory cytokines. It also blocks cholinesterase action also β-amyloid aggregation. Additionally, it exerts anti-hyperglycemic effect.
It is a saponin. It reduces osteoblast dysfunction due to the oxidative injury. It also enhances neuronal differentiation and induces type-1 collagen expression. It inhibits any spontaneous contraction of intestinal smooth muscle thus effective against diarrhea.
It offers significant neuroprotective effect against Aβ(25 – 35) peptide induced apoptosis in neuronal PC12 cells. Further it helps improve cognitive deficits provoked by injecting Aβ(25 – 35) peptide in mice. It is now considered to use for treating Alzheimer’s disease.
Large beneficial effects on various nervous disorders: 1) Powerful anti-epileptic behavior enhancing the level of GABA; 2) prevents Alzheimer’s disease by protecting hippocampal cells; 3) Prevents Parkinson’s disorder by enhancing the dopamine level within striatum; 4) Anxiolytic effect; 5) antidepressant; 6) Anti-ischemic effect in brain injury; 7) Prevents / cures vascular dementia by enhancing Acetylcholine level in brain / CNS neuron.
Pharmacological effects: Numerous studies on AC indicate that the plant exerts versatile bioactivities due to the presence of large reserve of different types of phytochemicals. Several important effects are briefly discussed below.
Anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive effect – Both in vivo and in vitro studies confirmed that the ethanolic extract of AC rhizomes and leaves have strong immunomodulatory and antiinflammatory role. It inhibits the proliferation of mitogen and antigen activated human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Its antiinflammatory action is due to inhibition of IL-8 and IL-6 also reduction of NF- κβ. Further investigation reveals that the extract prevents the generation of several pro-inflammatory cytokines via multiple pathways. On that perspective AC is obviously a novel anti-inflammatory agent. It is also noticed that the extract can reduce the neuropathic pain in laboratory animals. The effect could be due to multiple actions of antiinflammatory, anti-oxidative and neuroprotective agents in AC.
Antimicrobial and antifungal effect – Both leaves and rhizomes extract display antifungal and antimicrobial activity but it is ineffective in the case of E coli. The identifiable compounds are α – and β- Asarone. It can also act as anthelmintic agent. Further, AC synthesizes the enzyme, Heme peroxidase which also takes part during antifungal defense. The enzyme has significant role against the growth of number of phyto-pathogens.
Antimalarial activity – AC extract has potent antimalarial role when tested against Plasmodium falciparum (3D7 strain). The identifiable component is β –Asarone. Structure factor relationship shows that 2, 4, 5 –tri-methoxy groups on phenyl ring exerts the major reactivity.
Antidiabetic effect – The extract of AC shows considerable effect. The hypoglycemic action is due to the release of insulin and subsequent inhibition of α- glycosidase. The anti-diabetic study shows that oral administration of the extract can restore the plasma glucose level in Streptozotocin induced diabetic animals. The experiment further indicates that after three weeks of treatment the level of LDL, lipid and Glucose 6 – phosphatase, fructose 1, 6 – phosphatase and other marker enzymes considerably go down in diabetic induced animals. Despite the fact that some of the phyto-chemicals within AC have hypoglycemic effect but no exact component(s) is not identified yet.
Neuroprotective effect and Alzheimer’s disease – It has been documented that AC extract provides protective effect by preventing the neuronal damage. The extract helps restore the cognitive function in brain injury sufferers. One of the identifiable compounds is β- Asarone. Using animal model, it is established that β-Asarone can prevent or reduce the Aβ (1-42 peptide) induced neuronal damage within hippocampus [Alzheimer’s animal model] of rat by down regulating BcL-2, BcL-w, Caspase-3 activation and c-jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) phosphorylation. The in vitro experiment using Aβ peptide injected cultured neuronal cells also supports the fact.
The generation of free radicals is basically the underlying reasons behind many neurodegenerative diseases and cognitive impairments. The root or rhizome extract is used in the treatment for a long period of time. The major active principle(s) has been identified later to be α – and β – Asarone. Both work by blocking the NMDA receptor channel. α– isomer is seen more potent to inhibit the binding of [H3] – MK-801 to NMDA receptor, which could be consistent with its neuroprotective role. Studies also confirmed that both α- and β – isomers enable to provide protection against Glutamic acid induced excitotoxicity while blocking the NMDA receptor function. Additionally, the extract causes significant improvement in neurobehavioral performances. The other experiments indicate that AC extract holding numerous constituents exerts neuroprotective effect during ischemia in brain as proven in the rat model.
Antioxidant activity – Abundant studies establish the large potential of AC regarding its antioxidant role. Laboratory experiments demonstrate that AC can inhibit Fe+3 induced epileptogenesis by modulating the antioxidant enzymes indicating the beneficial use of AC extract as an effective anti-epileptic agent. The extract can prevent the radiation induced DNA and cell membrane damage. In vitro experiments also confirm that the extract can inhibit the lipid peroxidation.
Adipogenic action – It has been identified that β-Asarone in AC might inhibit adipogenesis. The compound suppresses the expression of adipogenic transcription factors. In vitro works also show that AC extract inhibits adipogenesis and subsequently stimulates the lipolysis in 3T3-L1 adipocyte cell line. Additionally, Asarone can lower intracellular triglyceride level while stimulating phosphorylation of hormone sensitive lipase that triggers the lipolysis in adipocytes. Considering the overall aspects, AC extract shows potential in treating type-2 diabetes.
Blood pressure lowering effect – The extract of AC shows blood pressure lowering effect including the vascular modulator ability. Experiments indicate the involvement of several constituents in AC following different pathways. Among them relaxant effect is mediated via the Ca+2 antagonism plus NO pathways causing the reduction of blood pressure whereas the vasodilatory effect is caused by different manner. So, AC is established to be antihypertensive, circulatory stimulant and vascular modulator.
