Introduction
In the vast kingdom of fungi, few species have captivated the human imagination and stirred scientific curiosity quite like the Amanita genus. A potent mix of beauty, mystery, and power, Amanita mushrooms are renowned not just for their iconic aesthetics but also for the array of bioactive compounds they harbor. This diverse group of fungi, which includes the well-known Amanita Muscaria, Pantherina, and Regalis, is a cornerstone of mycology, the study of fungi, warranting our attention and exploration.
Significance of the Amanita Genus in Mycology
Amanita mushrooms hold a paramount position in mycology due to their rich bioactive compound profile, their distinctive appearances, and their complex interactions with the environment. The study of these fungi provides invaluable insights into ecological relationships, biochemical processes, and potential applications in fields like health and wellness. Among the various Amanita species, Muscaria, Pantherina, and Regalis are particularly noteworthy. Their striking appearances, combined with intriguing bioactive properties, make them significant subjects of scientific and cultural exploration.
The Need for Understanding Bioactive Compounds
Understanding the bioactive compounds present in Amanita mushrooms is crucial for numerous reasons. First, these compounds play pivotal roles in the mushrooms’ life processes, thereby helping us better comprehend their biology and ecology. Additionally, these compounds carry potential implications for human health and wellness. Amanita mushrooms, like Muscaria, Pantherina, and Regalis, contain various bioactive compounds such as muscimol, ibotenic acid, and muscaridine, to name a few. These compounds have been associated with diverse effects, from psychoactive properties to potential therapeutic applications. A comprehensive understanding of these compounds opens the doors to their possible uses, potentially contributing to the realms of medicine, nutrition, and holistic wellness. As we delve deeper into the Amanita mushroom compounds in this article, we’ll illuminate their mysteries and reveal their potential, offering a detailed, comprehensive exploration of these fascinating fungi.
Spotlight on Amanita Species: Muscaria, Pantherina, and Regalis
As we embark on our journey into the world of Amanita mushrooms, we spotlight three fascinating species: Amanita Muscaria, Amanita Pantherina, and Amanita Regalis. Each of these species carries its own unique set of characteristics, cultural significance, and habitats, distinguishing them in the vast field of mycology. Let’s delve deeper into each species to understand their individual stories and why they hold a special place in our exploration of Amanita mushroom compounds.
Historical and Cultural Importance of Each Species
Amanita Muscaria, also known as the fly agaric, is probably the most iconic of all mushrooms. It’s easily recognized by its vibrant red cap with white spots, frequently seen in illustrations of fairy tales and folklore. Historically, it has been associated with shamanistic practices in Siberia and has sparked intrigue due to its psychoactive properties.
Amanita Pantherina, or the panther cap, is another species with historical importance. Despite being less conspicuous than its red-capped cousin, it has been used in traditional medicine in some cultures, and its psychoactive properties have been the subject of scientific and cultural curiosity.
Finally, Amanita Regalis, also known as the royal fly agaric, may not be as universally recognized as the Muscaria, but it holds its own importance in the northern regions of Europe, Asia, and North America. Its brown cap distinguishes it from the Muscaria, and its use in traditional medicine and cultural practices underscores its relevance.
Distinguishing Features of Each Mushroom
Each Amanita species carries a unique set of physical traits that set them apart. Amanita Muscaria is famed for its bright red cap adorned with white spots, a white stem, and gill structure. Amanita Pantherina is similar in shape but has a brown cap, often with a metallic sheen, and fewer warts. Amanita Regalis, on the other hand, is often darker, with a brown cap and white or yellowish warts.
Habitat and Distribution
Amanita Muscaria, Pantherina, and Regalis have diverse geographical ranges, but they share a common trait: they form symbiotic relationships with various tree species. Amanita Muscaria is common in the northern hemisphere but has been introduced to other regions, including the southern hemisphere. Amanita Pantherina, initially found in Europe, has now spread to other continents. Amanita Regalis is most common in the boreal regions of Europe, Asia, and North America. Understanding their distribution and habitat helps us contextualize their role in the ecosystem and their interaction with other species.
With this understanding of each species’ cultural, historical, and biological significance, we can now delve deeper into the bioactive compounds that these Amanita mushrooms house and their potential implications and applications.
Demystifying Bioactive Compounds
In the rich tapestry of life on Earth, one thread weaves a particularly fascinating story: the bioactive compounds found in mushrooms, particularly the Amanita genus. These compounds, far from being mere chemical constituents, play pivotal roles in the organisms’ defense, propagation, and interactions with their environment. More importantly, they influence human physiology in ways that have captured the interest of scientists, medical professionals, and enthusiasts alike.
Introduction to Bioactive Compounds
Bioactive compounds are chemical constituents produced by organisms that have biological effects on other organisms. They are a focal point of interest in numerous fields of study, including pharmacology, mycology, and environmental science. The compounds’ diverse structures and mechanisms of action enable them to interact with a variety of biological targets, influencing physiological and biochemical processes.
In the Amanita genus, the principal bioactive compounds are muscimol and ibotenic acid, but several others also contribute to the unique properties of these fungi. These compounds, residing mainly in the mushroom’s cap, distinguish these fungi as both mesmerizing and mystifying.
Their Role in Fungal Potency
The bioactive compounds found in Amanita mushrooms serve key functions that contribute to the fungi’s potency. Muscimol, a psychoactive compound, and ibotenic acid, a neurotoxic prodrug, are the primary contributors to the psychoactive properties of these mushrooms. These compounds act as the fungi’s defense mechanism, deterring predation and potentially inhibiting the growth of other competing organisms.
Additionally, these compounds facilitate a deeper connection between these fungi and their environment, influencing their symbiotic relationships with various tree species and other organisms. Understanding the role of bioactive compounds in these mushrooms gives us insight into their survival strategies and their niche in the ecosystem.
Impact of Bioactive Compounds on Human Physiology
The impacts of Amanita bioactive compounds on human physiology are manifold and complex. On ingestion, these compounds interact with various receptors in the human body, most notably the GABA and glutamate receptors in the nervous system. This interaction can induce a range of psychoactive effects, from altered perception and mood to hallucinations. However, hallucinations should not be expected when consuming amanita products. Most consumer research products have removed most of the ibotenic acid for safety and consuming large amounts most often results in deep sleep with vivid dreams.
On a more somber note, the compounds, especially if ingested in high amounts, can be neurotoxic, leading to potentially harmful effects. Thus, while Amanita mushrooms have found use in traditional medicine and cultural practices, they should be approached with caution due to these potent bioactive compounds. However, most consumer research products such as the amanita gummy or amanita capsule have been made safer by utilizing amanita mushrooms that have been decarbed to remove ibotenic acid.
As we move forward, we will explore each of these compounds in depth, their presence in the Amanita Muscaria, Pantherina, and Regalis, and what ongoing research suggests about their potential applications and risks. Stay tuned as we journey into the heart of the Amanita mushroom kingdom.
Deep Dive into Amanita Muscaria: Muscimol and Ibotenic Acid
The forest floor’s red and white speckled beauty, Amanita Muscaria, offers more than just visual delight. Hidden within its cap are the powerful bioactive compounds Muscimol and Ibotenic Acid. These two compounds, with their unique structures and impacts, have shaped the reputation and uses of this famous mushroom.
Structural Analysis of Muscimol and Ibotenic Acid
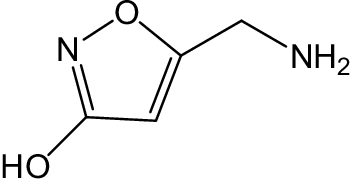
Muscimol, scientifically known as 5-(aminomethyl)-3-isoxazolol, is a psychoactive compound found in the Amanita Muscaria. Its structure, characterized by an isoxazole ring attached to an aminomethyl group, is a key contributor to its potency.
Ibotenic acid, or α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-isoxazoleacetic acid, is a neurotoxic prodrug that is also present. It shares structural similarities with two important neurotransmitters in the human brain: glutamate and GABA. The presence of the isoxazole ring and the carboxylic acid group in ibotenic acid plays an integral role in its neurotoxicity.
Biological Function and Impact on Human Physiology
Muscimol and ibotenic acid interact differently within our bodies. Ibotenic acid acts as an agonist for certain types of glutamate receptors, called NMDA and AMPA receptors. On the other hand, Muscimol acts primarily on GABA receptors, the primary inhibitory neurotransmitters in the human nervous system.
This interaction with the central nervous system leads to a wide range of effects. At lower doses, these effects might include euphoria, altered visual and auditory perceptions, and a sense of increased clarity. At higher doses, it can cause drowsiness, hallucinations, muscle spasms, and in extreme cases, seizures, or unconsciousness.
Traditional and Modern Uses of Amanita Muscaria
The Amanita Muscaria, steeped in folklore and tradition, has been utilized for centuries. Historically, it found use in shamanistic practices in Siberia and other northern cultures. Shamans consumed the mushroom to enter trances and connect with the spiritual realm. It’s also speculated that the mushroom played a role in Viking ‘berserker’ rituals due to its psychoactive properties.
In modern times, the Amanita Muscaria has been explored for its potential therapeutic applications. Some research suggests that it may hold potential for the treatment of neurological disorders, like Alzheimer’s disease, due to the compounds’ interaction with GABA and glutamate receptors.
Nonetheless, it’s crucial to remember that these mushrooms, while fascinating, can also be dangerous due to their psychoactive and neurotoxic compounds. Responsible use and an understanding of their effects are key to safely exploring the world of Amanita Muscaria.
As we move further, we shall dive into the intriguing compounds found in Amanita Pantherina and Amanita Regalis and understand their significance in our natural world.
Unraveling the Mystery of Amanita Pantherina: Spotlight on Pantherine
When we shift our focus to Amanita Pantherina, a close relative of Amanita Muscaria, the star player in its composition is the bioactive compound Pantherine. This mysterious compound and the mushroom itself have captured the interest of mycologists and psychonauts alike, illuminating a unique path through the world of fungi.
Examination of the Pantherine Compound
Scientifically known as 5-aminomethyl-3-isoxazolol, Pantherine is structurally similar to Muscimol, the dominant compound in Amanita Muscaria. It contains an isoxazole ring attached to an aminomethyl group, the key to its bioactivity. This compound is an isomer of Muscimol, hinting at the close relationship between these two Amanita species.
Impact on the Human Body and Known Effects
Similar to Muscimol, Pantherine also affects the GABA receptors, influencing inhibitory signals in the central nervous system. However, the effects of Pantherine ingestion aren’t fully understood and can be unpredictable, making it a compound of interest in ongoing research.
Reported effects of Pantherine consumption range from sedation, perceptual changes, and muscle twitching to severe symptoms like convulsions at higher doses. Its psychoactive properties make it an intriguing subject for study, but they also signal caution for potential users due to their possible harmful effects.
Traditional and Modern Uses of Amanita Pantherina
The historical use of Amanita Pantherina is less well-documented than its cousin, Amanita Muscaria. However, it is believed that some cultures might have used this mushroom for its psychoactive properties, potentially in spiritual or shamanic contexts.
Today, Amanita Pantherina is primarily of interest for research purposes due to Pantherine and other bioactive compounds. While the mystery of Pantherine offers an intriguing area for scientific exploration, its potential toxicity makes responsible usage critical for those interacting with Amanita Pantherina.
With an understanding of Pantherine’s role in the unique attributes of Amanita Pantherina, we now turn to another member of the Amanita family: Amanita Regalis, and its primary compound, Bufotenin. Let’s continue our journey through the biochemical universe of Amanita mushrooms.
Journey into Amanita Regalis: Exploring its Bioactive Compounds
As we trek further into the Amanita genus, our next destination is Amanita Regalis, commonly known as the Royal Fly Agaric. Though it shares a similar appearance to Amanita Muscaria, its bioactive compounds and effects differentiate it in significant ways, offering another fascinating lens into the complex world of fungi.
Analysis of Compounds in Amanita Regalis
Amanita Regalis boasts an array of bioactive compounds, with the key players being Muscimol, Ibotenic acid, and to a lesser extent, Bufotenin. The latter, a tryptamine related to the neurotransmitter serotonin, is of particular interest due to its psychoactive properties and less frequent occurrence in the Amanita genus.
Comparison to Amanita Muscaria's Compounds
While Amanita Regalis shares Muscimol and Ibotenic acid with Amanita Muscaria, their quantities differ. Amanita Regalis typically contains lower levels of these compounds, but a higher concentration of Bufotenin. This unique chemical makeup results in a different psychoactive profile, distinguishing it from its red-capped cousin.
Interestingly, Bufotenin has a similar structure to other psychedelic compounds, such as DMT and psilocin. The presence of this compound potentially contributes to the unique psychoactive effects of Amanita Regalis, though the precise nature of its contribution remains an area of ongoing study.
Traditional and Modern Uses of Amanita Regalis
While the historical record on the usage of Amanita Regalis is sparse, it’s thought that the mushroom may have been used in similar contexts as Amanita Muscaria due to its similar psychoactive properties. Given its lower concentrations of Muscimol and Ibotenic acid, however, its effects would likely have been less potent.
In modern times, Amanita Regalis is primarily used in scientific research, as its combination of psychoactive compounds provides a unique focus for study. As with other Amanita mushrooms, caution is advised due to potential toxicity and unpredictable effects.
Understanding Amanita Regalis’ distinctive compounds wraps up our exploration of the major species in the Amanita genus. Next, we delve into the potential medical applications of these fascinating fungi, showcasing their untapped potential in the field of medicine.
Comparative Analysis: The Bioactive Compounds Across Amanita Muscaria, Pantherina, and Regalis
As we further delve into the world of Amanita mushrooms, it becomes increasingly clear that each species carries its unique blend of bioactive compounds, presenting different effects and potentials for medicinal applications. This section offers a comparative analysis, highlighting the differences and similarities across Amanita Muscaria, Pantherina, and Regalis.
Detailed Comparison of Compounds Across the Species
Amanita Muscaria and Regalis both share the presence of Muscimol and Ibotenic Acid, with Muscaria having higher concentrations of both. Amanita Pantherina, on the other hand, is distinct for its higher levels of Pantherine, a compound that shares a similar structure with Muscimol but exhibits different physiological effects. Amanita Regalis stands out for its presence of Bufotenin, a compound not typically found in the other two species.
The Effects and Potency of Each Species
The potency and effects of these mushrooms largely depend on their individual profiles of bioactive compounds. Amanita Muscaria, with its high concentration of Muscimol and Ibotenic Acid, tends to have the most potent psychoactive effects. Amanita Pantherina’s effects are primarily attributed to Pantherine, leading to different psychoactive experiences. Amanita Regalis, with lower levels of Muscimol and Ibotenic Acid but a higher concentration of Bufotenin, offers a distinct psychoactive profile.
Potential Medicinal Applications of Each Species
Each Amanita species offers unique potentials for medicinal applications. Amanita Muscaria’s high concentrations of Muscimol have been of interest in neuropharmacological research, particularly in studying the GABAergic system. Amanita Pantherina’s Pantherine shows potential for its anticholinergic effects.
Amanita Regalis, with its distinct presence of Bufotenin, offers potential for studying the role of serotonin-like compounds in the human brain. However, it’s important to underscore that these potential applications are still largely under research, and consumption of these mushrooms outside controlled environments can be dangerous due to their toxicity and unpredictable effects.
As we conclude our comparison, it’s clear that these three Amanita species, though sharing a genus, present different bioactive compounds leading to different potencies, effects, and potential uses. This complexity underscores the fascinating diversity within the fungi kingdom and sets the stage for future exploration and discovery.
The Amanita Experience: Impact of Bioactive Compounds
The Amanita mushroom species, known for their calming properties, have enthralled humanity for centuries. From shamanic rituals to modern therapeutic exploration, these species’ distinctive profiles of bioactive compounds have played a central role in these contexts. In this section, we’ll take you through the psychoactive effects of Amanita compounds, their role in traditional practices, and the modern interest in these species for potential therapeutic use.
The Psychoactive Effects of Amanita Compounds
The psychoactive effects of Amanita mushrooms are primarily due to compounds like Muscimol, Ibotenic Acid, and Pantherine. These compounds interact with our nervous system, particularly with the GABA and glutamate neurotransmitter systems, inducing effects that range from mild euphoria and altered perception to more intense experiences of hallucinations and delirium. It’s essential to note that these effects can vary significantly based on dosage, preparation, and individual physiology.

A normal does will provide the effects of mild euphoria that helps with everyday life.
The Role of Amanita Species in Shamanic Practices
For centuries, Amanita mushrooms have found their place in various cultures’ spiritual and shamanic practices. Most notably, the Siberian tribes have utilized Amanita Muscaria in their rituals, seeking its mind-altering effects for spiritual journeys and divination. Amanita Pantherina and Regalis, while less documented, are also believed to have been used in similar contexts.
Modern Interest in Amanita for Therapeutic Use
In the wave of psychedelic renaissance, the Amanita genus has caught the attention of modern researchers and psychonauts. Inspired by their traditional use and intriguing psychoactive profiles, there’s growing interest in exploring the potential therapeutic applications of these mushrooms. From studying the GABAergic action of Muscimol for potential neuropharmacological applications to the serotonergic potential of Bufotenin in Amanita Regalis, the exploration is far from over. It’s crucial, however, to remember that the consumption of Amanita mushrooms comes with risks, and their use should always be guided by respect, caution, and rigorous science.
The Amanita experience, deeply rooted in the interaction between bioactive compounds and our physiology, takes us on a fascinating journey from traditional shamanic practices to the frontiers of modern psychedelic exploration.
Safety First: Essential Guidelines for Studying and Using Amanita Mushrooms
The world of Amanita mushrooms is intriguing, but it’s crucial to approach these potent organisms with the utmost respect and caution. In this section, we underscore the importance of safety measures and precautions, dosage considerations, and the need for responsible and ethical use of Amanita species.

Safety Measures and Precautions
Handling and using Amanita mushrooms should always be preceded by comprehensive knowledge and understanding of the species. As different Amanita species possess different potencies and toxicity levels, accurate identification is key to safe usage. It’s also important to be aware that these mushrooms can have variable effects on different individuals and can interact negatively with certain medications or pre-existing health conditions.
Always ensure you’re sourcing your mushrooms from reliable and knowledgeable sources. For those interested in foraging, obtaining training from experienced mycologists or participating in guided mushroom hunts can minimize the risks.
Dosage Considerations for Each Species
Dosage is another critical safety aspect. The potency of Amanita mushrooms can vary significantly, not only between different species but also between different specimens of the same species, depending on factors like age, size, and habitat conditions. As a general rule, it’s best to start with small doses and closely monitor the effects before considering a higher dose. This will also depend if you are consuming amanita gummies, capsules or powder.
Also, it’s worth noting that the psychoactive compounds in these mushrooms can take a while to metabolize in the human body, so it’s crucial to wait a sufficient amount of time before taking an additional dose to avoid unintended overdosing.
Responsible and Ethical Use of Amanita Species
The potential psychoactive effects of Amanita mushrooms can be powerful and profound. However, these effects can also be unpredictable and sometimes unpleasant or even dangerous. Responsible use involves understanding these risks and approaching these mushrooms with respect and caution.
Ethical use also involves an awareness of the ecological role these mushrooms play. When foraging, it’s important to do so sustainably, leaving plenty of specimens behind to ensure the continued health and diversity of the local mycological ecosystem.
In summary, venturing into the world of Amanita mushrooms should always be guided by a safety-first approach. By doing so, we can continue to unravel the mysteries of these remarkable organisms in a responsible and respectful way.
Conclusion
The enchanting world of Amanita mushrooms offers a profound blend of history, cultural importance, and scientific intrigue. As we draw this exploration to a close, let’s look forward to the future, recap the key points of our journey, and encourage you, dear readers, to further engage with the field of mycology.
The Future of Amanita Research: Potential and Prospects
The bioactive compounds found in Amanita mushrooms hold untold potential. As research progresses, it’s likely that our understanding of these compounds and their medicinal applications will evolve significantly. Scientists and researchers worldwide are working tirelessly to decode the mysteries hidden in these mushrooms, paving the way for potential breakthroughs in fields like neurology, psychiatry, and more.
Summary of Key Points
In this journey, we delved deep into the heart of three captivating Amanita species: Muscaria, Pantherina, and Regalis. We examined the historical significance of these species, their bioactive compounds, and their influence on human physiology. We explored the traditional and modern uses of these species, conducted a comparative analysis of their compounds, and underscored the need for safety and ethical use of these potent organisms.
Encouragement for Readers to Engage with Mycological Studies
The world of mushrooms is as fascinating as it is vast. Amanita species, with their intriguing bioactive compounds, are just the tip of the iceberg. We encourage you, our curious readers, to explore further, dig deeper. Engage with mycological studies, be it through academic pursuits, amateur mushroom hunting, or simply staying informed about the latest research. Your interest and participation can contribute to the understanding and appreciation of these unique organisms.
In conclusion, the Amanita genus holds a treasure trove of secrets, waiting to be unveiled. As we move forward, we anticipate a future of discovery, learning, and an ever-deepening appreciation for the complexities and wonders of the mycological world.
Read More:
Unlocking Relief: The Role of Amanita Muscaria in Alleviating Depression
Discover the potential of Amanita Muscaria in easing depression symptoms.
Read MoreSafety First: Assessing the Risks of Amanita Muscaria Capsules
Delve into the world of Amanita Muscaria capsules and uncover...
Read MoreDIY Amanita Capsules: A Step-by-Step Guide
Discover how to create your own Amanita capsules with our...
Read MoreCheap Muscimol Isolate: Quality at a Discount
Discover the secret to high-quality muscimol isolate at an affordable...
Read More









